Imagine that you have not just a program but a digital employee who understands what you want, finds solutions, and brings things to life. This is agentic AI — a new type of artificial intelligence that doesn’t wait for step-by-step instructions but acts autonomously: analyzing data, making decisions, and performing human-level tasks. It adapts, learns, and works for results — even if conditions change.
Such smart agents are becoming increasingly popular because it is no longer enough for businesses to simply automate processes. Today, it’s important to act quickly, flexibly, and with minimal human involvement.
Thanks to the development of generative AI and powerful language models, agentic AI is already available and can dramatically improve efficiency, from customer service to strategic tasks.
What is Agentic AI: Evolution from Traditional AI to Intelligent Agents
Research company Markets & Markets estimates that the agentic AI market will grow from $13.8 billion in 2025 to $140.8 billion by 2032. This means that the demand for intelligent agents will grow more than 10 times in a few years.
This growth is a result of the fact that businesses and users are no longer satisfied with “smart” programs — they want solutions that not only take commands but understand objectives, are able to take independent action, and adapt to changing circumstances.
Unlike traditional AI, which responds to a specific request (for example, “tell a joke” or “analyze a spreadsheet”), agent-based AI can analyze a complex task, propose a solution, execute it, and adapt if something goes wrong.
| Characteristic | Traditional AI | Agentic AI |
| Focus | Solving a single task | Multi-step goals and strategies |
| Initiative | Reactive | Proactively determines next steps |
| Memory and Context | Limited | Long-term memory and learning from experience |
| Interaction with Environment | Passive | Active (observes, acts, learns) |
| Planning | None or limited | Multi-step, goal-driven planning |
| Example | Chatbot, image classifier | Agent that books an entire trip |
Comparison of traditional AI and Agentic AI
The role of an AI agent in such a system is not just to perform actions but to act as an active participant in the process. It knows what the main goal is, breaks it down into smaller tasks, studies circumstances, talks to the necessary services, and completes the task.
This approach is especially important in businesses that value not only speed but also adaptability. An agent can replace a whole chain of routine operations, reduce errors, and save time for employees.
Agentic AI and Generative AI: How These Approaches Interact
At first glance, it may seem that agentic AI and generative AI are two different directions in the field of artificial intelligence. However, in practice, they are closely related and complement each other.
Generative models, such as GPT, Claude, or Gemini, act as a “motor” that drives agentic systems. And agentic AI, in turn, turns these models into full-fledged autonomous executors.
Differences and Points of Intersection
Generative AI is a type that can create new content: text, images, music, code, and more. It relies on big data learning and is able to generate meaningful, coherent, and contextualized results at the user’s request.
Agentic AI uses such models as part of a more complex system, where text generation is only one of the components. The main task of agentic AI is to achieve a goal: to plan actions, perform the necessary steps, take into account feedback, and, if necessary, change behavior.
Here are the main differences:
| Characteristic | Generative AI | Agentic AI |
| Purpose | Content creation | Task execution and goal achievement |
| Behavior | Reactive: responds to prompts | Active: determines actions independently |
| Memory and Context | Limited or single-use | Long-term, considers previous actions |
| Planning | Absent | Built-in planning and course correction |
| User Interaction | Through individual prompts | Through interactive and ongoing dialogue |
Differences between Generative AI and Agentic AI
Thus, generative AI can be seen as a tool, and agentic AI can be seen as the architect that manages that tool.
Benefits of Agentic AI: More Than Just Automation
Agentic AI gives businesses more than just a convenient tool to speed up processes — it changes the very approach to work. Such systems become full-fledged participants in making decisions, adapting to changes, and increasing business resilience to external challenges.
Improved Efficiency and Speed of Processes
Instead of performing only individual operations (e.g., sending an email or generating a report), agent-based AI is able to take over the entire chain of actions: from understanding a task to monitoring its fulfillment. This can reduce the time to complete tasks on time and free employees from routine chores.
Companies that have already implemented AI agents see efficiency gains of up to 55% and cost reductions of up to 35%.
Resilience to Uncertainty
Agentic AI is able to work in conditions where there is no clear instruction or unforeseen situations arise. It doesn’t “hang up” on non-standard inputs but replans actions, clarifies details, and turns to external sources to find a solution.
Real-time Decision Making
Unlike traditional systems, agentic AI can not only perform a task but also assess the situation as it progresses, making decisions on the fly. For example, if a customer doesn’t respond to an email, the agent can remind them, suggest another way to contact them, or delegate the task to a human.
Scalability and Adaptability
A single agent can handle dozens of tasks simultaneously, and can be scaled and trained on the fly if necessary. As your company grows, you don’t need to hire hundreds of new employees for routine tasks — just “hire” new agents. Moreover, such systems adapt to changes in data, user preferences, or the external environment, without the need to rewrite code.

Types of Agentic AI Systems and How They Work
There are several types of agentic AI systems, each with its own level of complexity and autonomy. For example, reactive agents operate on a simple “if A, then B” principle — like an auto-responder or a basic chatbot.
More advanced goal-driven agents can take on complex tasks (such as “schedule a meeting”), create a plan, and carry it through to completion.
One step further are learning agents, which analyze their own mistakes and adjust their behavior over time.
In large-scale systems, multiple agents can work together, each responsible for a specific part of the process — this is known as a multi-agent architecture, commonly used in logistics, project management, and data analysis.
Agentic AI System: Architecture and Components
For an agent to act as an “ intellectual actor,” it must include several key components. Together, they provide perception, thinking, decision-making, and action.
Intelligent Agent Architecture
In a standard agentic AI system, the following levels are typically present:
- Goal module: Determines what needs to be done. Receives the task from the user or other systems and formulates the final goal.
- Planner: Breaks down the goal into steps, prioritizes, and selects an appropriate strategy to achieve the outcome.
- Executor: Performs actions — it can interact with the API, send emails, update documents, or execute commands in the UI.
- Monitor/Observer: Monitors results, checks against goals, reports errors, or the need to adjust the plan.
- Reasoning Engine: Analyzes options, finds optimal solutions, especially in situations with uncertainty.
- Memory: Stores data, context, past experiences, and outcomes of actions — both short and long term.
Agentic AI Use Cases: Where the New Approach Already Works
Although the concept of agentic AI has been actively developing over the past 1-2 years, real examples of its implementation are already found today in a wide range of spheres, from finance to medicine. Here is how it works in practice.
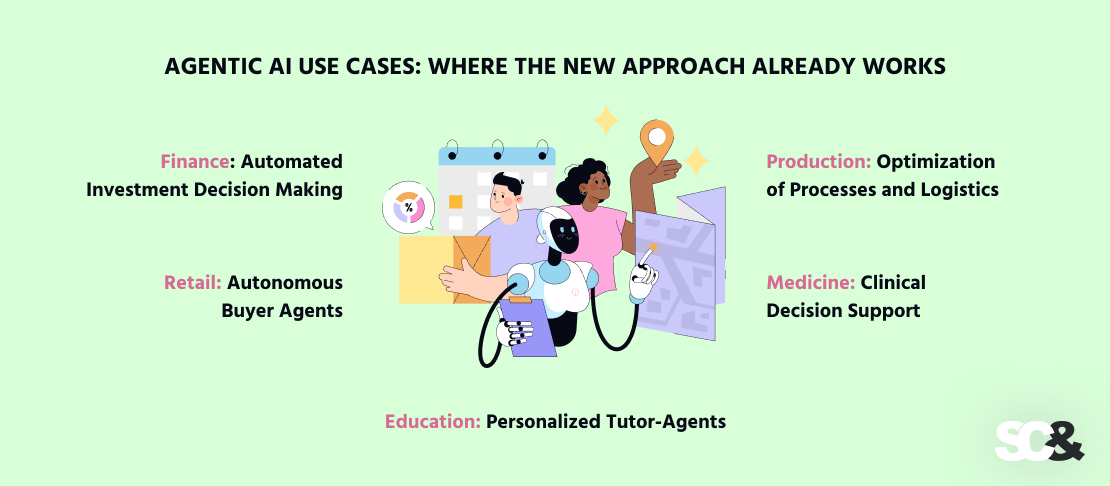
Finance: Automated Investment Decision Making
In investment companies, agent-based systems help build and manage portfolios based on real-time market analytics. Such agents do not just process data but also monitor news, analyze dynamics, and suggest or make decisions on strategy changes — for example, re-allocate assets when volatility increases or replace them in response to corporate events.
Retail: Autonomous Buyer Agents
In e-commerce, companies can use AI buyer agents to act on behalf of customers. They can select products according to preferences, find favorable offers, compare parameters, and even place an order, pay, and track delivery themselves. And on the other hand, sellers use agents to manage inventory, pricing, and recommendations in real time.
Education: Personalized Tutor-Agents
EdTech can benefit from AI tutors that do not just answer questions but plan a study route for a particular student, select tasks according to knowledge level, monitor progress, and adapt the presentation of material.
Such agents are especially useful when learning languages, programming, and mathematics, where gradualness and individual approach are important. Instead of plunging into a general course, a student gets a personal teacher working 24/7.
Production: Optimization of Processes and Logistics
In enterprises, agent systems manage equipment schedules, logistics, and supply. For example, an agent can identify supply chain disruptions, suggest alternative suppliers, or reconfigure production depending on raw materials and demand.
Such agents do not require constant monitoring and can cope well with a volatile environment, especially in conditions of supply disruptions or price increases.
Medicine: Clinical Decision Support
In clinics and hospitals, agentic AI is used to analyze medical data and make treatment recommendations. For example, an agent can review a patient’s medical history, match it with the latest medical protocols, compare it to similar cases, and suggest optimal steps to the doctor.
As a result, the physician receives not just a reference but a deep analysis, saving time on a manual check-up.
Developing Agentic AI: How an Intelligent Agent is Created
For an intelligent agent to truly act autonomously, make decisions, and adapt to changing conditions, it’s vital to be built on a solid technological foundation. Below are the key principles and tools needed:
- Fundamentals of Agent Development: Creating an agent begins with designing an architecture that includes purpose, planning, executing actions, and analyzing the result — all in one cycle.
- Using LLM and generative AI: Most intelligent agents are powered by large language models (LLMs) that allow them to understand tasks, generate answers, and reason.
- Integration with cloud platforms: Azure AI, AWS, and Google Cloud provide the necessary tools, APIs, and compute resources to deploy, scale, and secure agent-based solutions.
- The role of data, memory, and feedback: The agent uses data pipelines, stores context in memory, makes logical decisions, and learns by analyzing its actions through feedback loops.
Agentic AI Development Services: How to Choose a Developer
Choosing a vendor for agentic AI development is not just a matter of technical implementation. This decision determines how flexible, secure, and scalable your intelligent agent will be.
With more and more companies looking to integrate AI agents into their business processes, it’s important to understand that a customized solution almost always provides more value than using an out-of-the-box template agent.
Off-the-shelf solutions (for example, bots in CRM, marketing assistants, or embedded agents in Google Workspace) are convenient but are severely limited in logic, integration, and adaptation to unique processes.
A custom AI agent, on the other hand, is created precisely for the client’s business objectives, taking into account infrastructure, industry specifics, level of data access, and even corporate communication style. This is especially important for financial, healthcare, and manufacturing companies, where mistakes can be costly.
One of the key factors in choosing an AI developer is the ability to build the right architecture and ensure security. The modern agent works with sensitive data, connects to CRM, APIs, back-end storage, and cloud services. Therefore, the vendor must ensure that:
- Isolation of data execution and storage
- Access rights control
- Agent action audit
- Protection against the generation of malicious or incorrect content
A good agentic AI developer will not just connect LLM but will also create a fail-safe system with logging, fallback modes, and behavior scenario management. This is especially important when implementing agents that make real-time decisions: processing orders, interacting with customers, managing logistics, or offering legally relevant recommendations.

Which AI Development and Agentic AI Services Are in Demand
The following AI development and agentic AI services are in particular demand in the market today:
- Development of custom AI agents for department or team tasks (assistants in sales, support, finance)
- Integration of LLM agents with corporate databases and APIs
- Training of agents on internal company data (fine-tuning or RAG)
- Building multi-agent systems where several agents coordinate work: plan, check, fix
- Development of agent management interfaces — from chat rooms to visual dashboards.
Thus, you should choose a partner for an agentic AI project not on the principle of “who can generate text faster” but on the basis of who is capable of building a sustainable intelligent system customized for your business. It is important that it is not just a development team but a partner who understands AI ar
Custom AI & AI Agent Development Services from SCAND
SCAND offers full-cycle development of custom AI and agentic AI solutions — from ideation and prototyping to industrial implementation and scaling.
With more than 25 years of software development experience and a deep focus on artificial intelligence, SCAND creates intelligent algorithms that can not just execute commands but understand goals, make decisions, and adapt to the environment in real time.
The team specializes in building resilient architecture, integrating with business processes, connecting to internal APIs, and protecting data, which is especially important for enterprise projects in finance, logistics, medicine, and education.
SCAND offers customized LLM development services using state-of-the-art generative models (GPT, Claude, Gemini, etc.) and develops custom AI agents fully tailored to the client’s objectives.
As part of an integrated approach, the company implements a full stack: from building data pipelines and memory systems to reasoning modules and interaction interfaces.
This approach allows SCAND not just to implement technology but to create full-fledged agent ecosystems that increase efficiency, reduce the burden on employees, and accelerate decision-making.
The Future of Agentic AI: What Lies Ahead
Agentic AI is not just a short-term trend but a fundamental change in the approach to building digital systems.
In the next 3-5 years, we can expect AI agents to become an integral part of corporate infrastructure, taking over up to 30-50% of operational tasks, especially those requiring data processing, planning, and communication.
The next stage will be the development of autonomous multitasking agents capable of making collective decisions and building complex workflows without human intervention.
Such systems will manage projects, analyze risks, adapt to changes in real time, and operate under conditions of incomplete information. In response, companies will rethink organizational processes, and governments — approaches to digital governance and citizen services.
In this transformational environment, SCAND offers not just technology deployment but deep integration of agent systems into the customer’s business environment.
With expertise in custom AI development and LLM integration, SCAND helps organizations move from automating individual tasks to building flexible, adaptive agent ecosystems that can scale, evolve, and meet the demands of the future.