It’s wild to think how far phones have come in the past 20 years. In 2000, the most remarkable feature was the introduction of polyphonic ringtones; in 2005, it was the inclusion of built-in cameras and color screens; in 2009, it was the advent of touchscreens and app stores.
And in 2015, it was the integration of fingerprint recognition and mobile wallets (according to Deloitte, 47% of respondents now use their phones to pay for goods and services in-store).
However, modern smartphones are already capable of predicting our next word, recognizing faces, naturally bridging languages, and even editing photos. The driving force behind all this intelligence and autonomy comes largely from artificial intelligence (AI).
For smartphone manufacturers, in turn, the ability to offer a range of AI features is becoming extremely important. With the share of AI-capable smartphones expected to surge in the coming years, AI now represents a key selling point as part of any new product launch.
In this article, we’ll explore how AI works inside mobile devices, what technologies power it, and how to find an AI development company that can help bring intelligent features to your own mobile app.
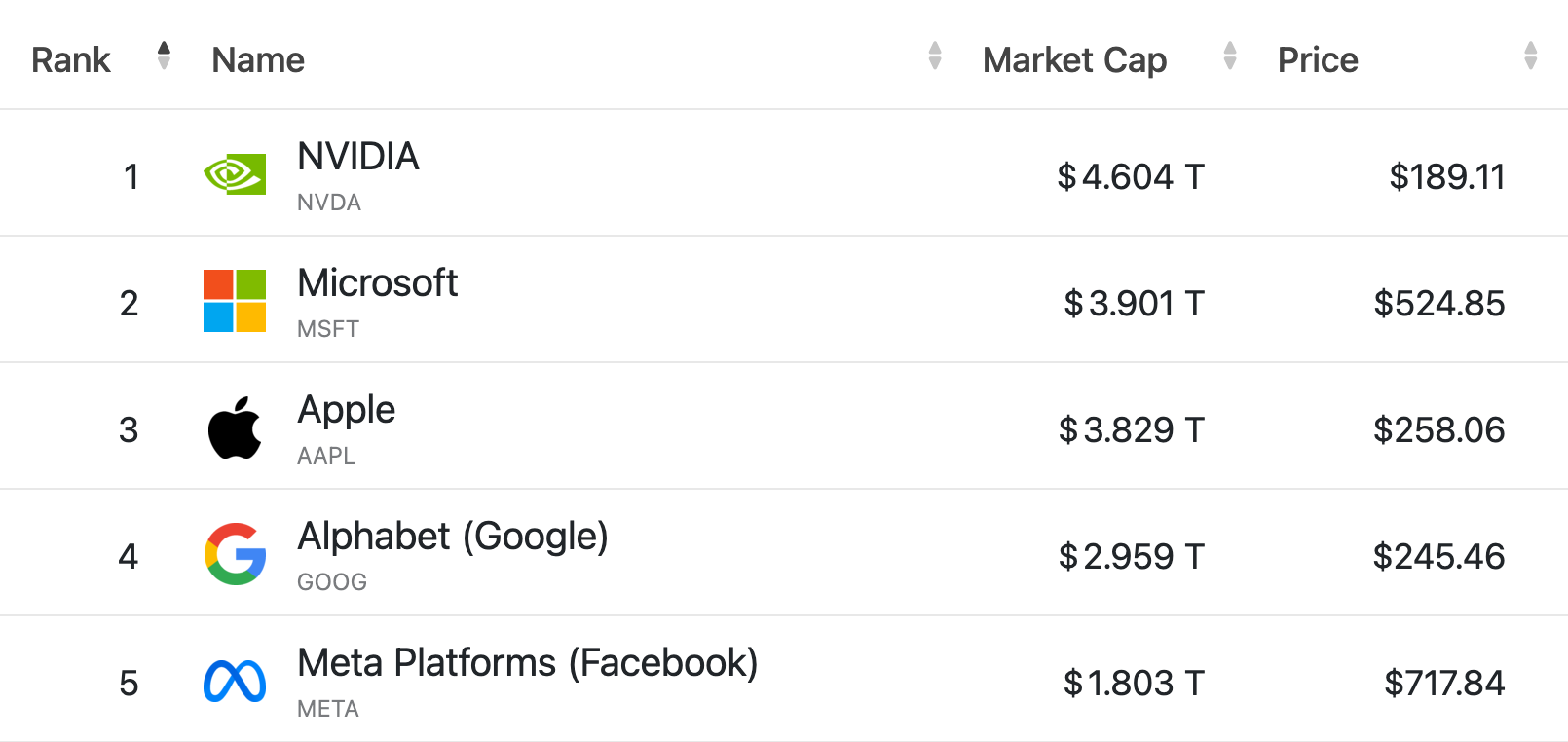
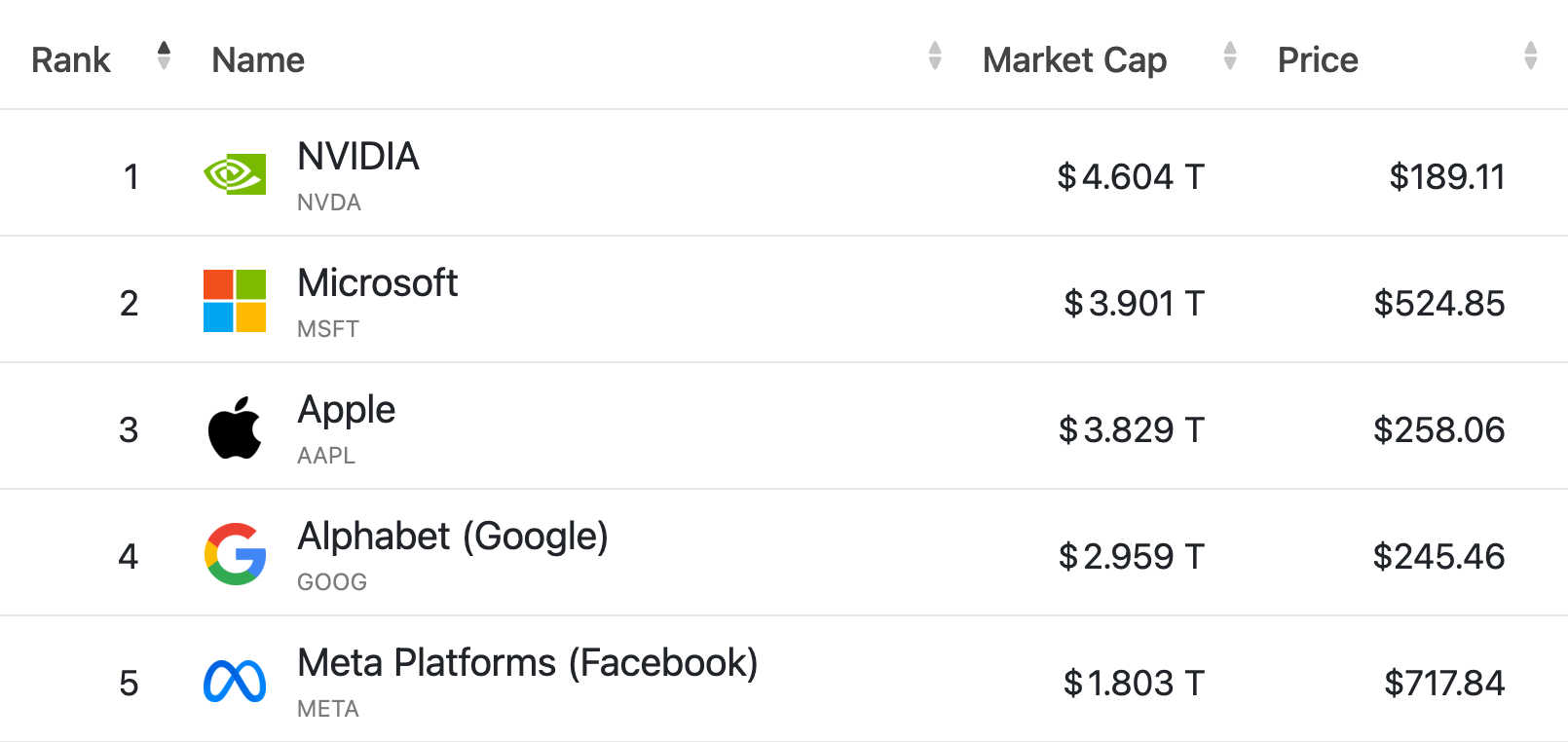
Leading AI Companies Globally 2025 by Market Cap, CompaniesMarketcap.com
What Is AI in Mobile Phones?
Essentially, AI on mobile devices means integrating intelligent algorithms into smartphones to let them learn from user behavior and perform things that were previously only possible with human-like reasoning.
The definition of an AI in smartphones has often focused more on the integration of AI-powered features and experiences rather than just the hardware.
Unlike AI-powered PCs, where the key marketing factor was the addition of a specialized AI chip or accelerator, the categorization of an AI-powered smartphone has typically been more about what it does for the user.
How Artificial Intelligence Works in Smartphones
AI functions can be executed either on the device or in the cloud.
- On-device AI processes data locally, which means faster responses, better safety, and offline capabilities.
- Cloud AI uses distant servers to run more complex computations, such as large-scale language models or live data analytics.
Most of today’s smartphones, though, use a hybrid approach, combining both to get the best performance and power management.
Besides, AI in phones relies on a series of underlying technologies — machine learning (ML), deep learning (DL), and neural networks — each with a different function.
- Neural networks mimic the structure of the human brain and serve as the foundation for most modern AI models.
- Deep learning is a more advanced form of neural networks that uses multiple layers to process complex inputs such as speech, images, and gestures — essentially scaling up traditional neural networks for higher performance.
- Large Language Models, a subset of deep learning, specialize in understanding and generating natural language. They’re now being adapted for mobile real-time text generation, translation, and conversational AI.
- Machine learning (ML) remains the broader field under which neural networks and deep learning operate.
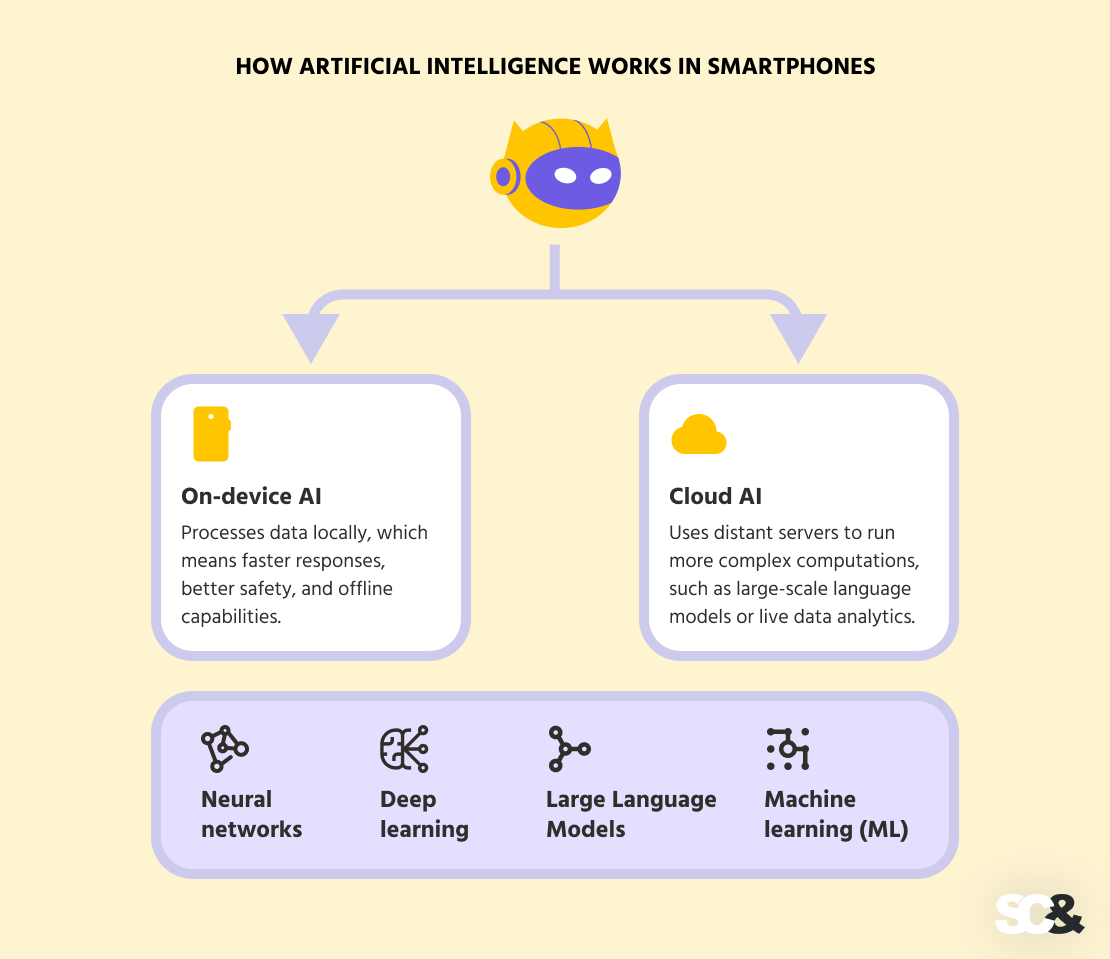
How AI Works in Smartphones
Leading AI Technologies Behind Modern Smartphones
Machine learning, deep learning, and neural networks don’t operate alone — they rely on specialized processing techniques and hardware to deliver real-world functionality.
Neural Processing Units (NPUs)
At the heart of AI-driven smartphones lies the Neural Processing Unit (NPU) — a dedicated chip for processing AI and ML workloads.
Unlike regular CPU or GPU chips, which handle general computing, NPUs are built to process many AI calculations at the same time. They power everything from photo processing and live translation to predictive typing and app suggestions.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP lets phones understand and respond to human language. It’s the core technology behind all popular voice assistants, helping them recognize what users say, understand what they mean, and reply naturally.
Modern NLP can even pick up on tone, context, and slang, making conversations feel more true-to-life. Besides voice commands, it also powers smart replies in messages, voice-to-text typing, and translations.
Computer Vision and Image Recognition
Computer vision gives smartphones the ability to “see” and understand what’s around them. With the help of deep learning and large amounts of image data, phones can recognize faces, objects, and scenes with impressive accuracy.
This technology powers many camera features we use every day — portrait mode, night photography, auto scene detection, Face ID, and visual search.
Edge AI
Edge AI means that a phone can process AI tasks directly on the device instead of sending data to cloud servers. This shift improves performance, reduces latency, and strengthens privacy since personal data never has to leave the phone.
Phones with special AI chips — like Apple’s Neural Engine or Google’s Tensor — use Edge AI to power real-time photo enhancement, instant translation, and predictive typing. In short, it helps a phone stay smart, quick, and secure — all on its own.
Everyday Applications of AI in Mobile Phones
Many leading smartphone manufacturers have demonstrated the potential of AI in smartphone user interfaces, showcasing a wealth of editing, assistance, and user experience tools accessible with a tap, swipe, or simply by voice.

Let’s look at how artificial intelligence works in practice across different areas of mobile use.
Mobile Photography and Videography
Smartphone cameras are among the most advanced uses of AI technology. AI-powered image processing uses convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to analyze lighting, color, and object composition in real time.
When individuals take a photo, the NPU in their phones runs numerous algorithms in milliseconds to determine the scene — landscape, portrait, or night shot — and automatically adjust exposure, white balance, and depth.
For portrait photography, AI uses semantic segmentation to separate the subject and dim the background in a way that simulates a DSLR’s blur. For low-light photography, multi-frame image stacking takes a series of shots and stacks them into one high-quality photo with less noise.
AI also supports HDR optimization and live video stabilization using predictive motion tracking.
Some phones, like Google’s Pixel series, even use computational photography techniques run by machine learning to recreate natural skin tones or remove unwanted objects from images.
Voice Assistants
Voice assistants such as Siri, Google Assistant, and Bixby employ natural language processing (NLP) and automatic speech recognition (Speech-to-Text, STT) to turn spoken words into machine-readable commands.
When users speak to the assistant, their voice is first analyzed through acoustic modeling in order to recognize phonemes — the most elemental sound units.
Then, language models interpret context and intent, turning phrases like “Remind me to call Alex at 6” into executable tasks.
AI also uses contextual learning, i.e., the assistant becomes intelligent with time through insights from past requests, calendar, and even geographical location.
For example, if a user repeatedly asks for the weather when leaving home, it can automatically start to give them that information.
Finally, Text-to-Speech (TTS) allows the assistant to generate natural, human-like responses directly on the device, making interactions more fluid and conversational without relying on cloud processing.
Predictive Text and Smart Typing
Behind every autocomplete suggestion lies a recurrent neural network (RNN) or transformer-based model trained on millions of language samples. These models predict users’ next word based on probability — learning from their typing patterns, frequently used phrases, and emoji preferences.
AI also powers intelligent autocorrect, which doesn’t just fix spelling but understands intent.
For instance, it knows a user meant “meeting” instead of “meting” based on sentence context. Over time, the keyboard adapts to their personal language style, improving accuracy with each use.
Personalization and Recommendations
AI continuously studies user interactions to deliver a personalized mobile experience. Using behavioral analysis, reinforcement learning, and contextual modeling, smartphones can predict specific needs in real time.
For example, a device can recommend apps that users frequently open at certain times of day or automatically switch to battery-saving mode when the battery is low.
Music and video apps use collaborative filtering, suggesting new content based on the user’s listening or viewing habits.
System-level personalization, such as adaptive brightness, uses the phone’s environmental sensors and AI models to learn specific preferences based on lighting conditions.
Security and Authentication
AI-powered security is normally based on biometric recognition and anomaly detection.

For Face ID or facial unlock, a phone captures a depth map and runs it through a 3D convolutional neural network (3D-CNN) trained to recognize unique facial characteristics, even when the appearance slightly changes.
Fingerprint recognition has also evolved: AI filters out noise from sensor data and applies pattern-matching algorithms for faster and more secure authentication.
Behavioral AI goes even further. Now it can analyze how people interact with their phones (typing speed, tilt, pressure) to catch suspicious activity or potential fraud.
Mobile Gaming and Augmented Reality (AR)
In gaming, AI controls non-player characters (NPCs) using decision trees, reinforcement learning, or behavioral modeling to create dynamic, responsive gameplay. These characters can adapt to a play style, making each session more realistic.
In augmented reality, AI improves spatial understanding through simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) — a process that helps a phone map physical spaces on the go.
Combined with object recognition and depth sensing, this allows apps like Pokémon GO or AR navigation tools to blend digital objects into the real world.
Automation
AI is more and more used to automate redundant tasks. With context-based triggers and rule-based ML, a phone can silence notifications during meetings, adjust power usage based on activity, or schedule routine maintenance in the background.
| Area | How AI Works | Examples / Features |
| Photography & Video | CNNs and NPUs adjust lighting, focus, and depth automatically | Scene detection, portrait blur, low-light stacking, HDR, video stabilization |
| Voice Assistants | NLP interprets speech and learns context | Siri, Google Assistant, Bixby; reminders, contextual suggestions |
| Predictive Typing | RNNs/transformers predict words and adapt | Autocomplete, emoji suggestions, context-aware corrections |
| Text Processing (LLM-powered) | Large language models summarize, rewrite, and generate text | Summarization, tone adjustment, smart replies, content generation |
| Personalization | Behavioral analysis tailors the experience | App suggestions, adaptive brightness, content recommendations |
| Security | Biometric and behavioral AI enhances safety | Face ID, fingerprint recognition, fraud detection |
| Gaming & AR | AI adapts NPCs and maps spaces in AR | Dynamic gameplay, AR apps like Pokémon GO, navigation tools |
| Automation | ML automates routine tasks | Smart notifications, battery optimization, task scheduling |
Key AI Applications in Mobile Phones
Benefits vs. Challenges of AI Algorithms in Smartphones
The vast majority of telecom operators view AI integration as a business imperative. As of 2024, nearly 90% of companies worldwide have fully or partially integrated this technology into at least one area of their business, while only 3% have no plans to do so.
Unsurprisingly, operators are generally looking to improve productivity. However, there are many other benefits for business.
For instance, AI proves to enhance device and app performance. Modern smartphones use dedicated hardware, such as Apple’s Neural Engine or Google’s Tensor, to run AI tasks efficiently on-device, reduce latency, save energy, and lower infrastructure and support costs.
Beyond performance, AI strengthens security and compliance. Deep learning improves fraud detection, identity verification, and behavioral authentication, while Edge AI and federated learning allow sensitive data to stay on-device, ensuring compliance with regulations.
Finally, AI boosts operational efficiency. It monitors systems, predicts potential issues, optimizes resources, and powers chatbots or virtual assistants to run routine tasks.
At the same time, adopting AI capabilities comes with several challenges. The first one is cost. Developing and maintaining AI systems requires specialized talent, high-performance hardware, and large datasets.
Smaller operators may struggle to make these investments while competing with large-scale players.
Besides, the wide range of possible AI applications has left organizations divided on where to direct resources, especially when the return on investment is difficult to quantify.
From a technical perspective, fragmentation in mobile devices is another problem. Different operating systems and hardware configurations can limit AI functionality or require developers to maintain multiple model versions.
Besides, complex AI models consume significant processing power and memory, potentially draining batteries or causing devices to overheat.
Of course, developers may use model pruning, quantization, and knowledge distillation to make models lighter and faster, but these steps add complexity to the development process.
Privacy and Ethical Considerations: Is It a Good Thing to Rely on AI
As artificial intelligence app development emerges as an integral part of mobile business strategies, companies also face increasingly growing privacy and ethical risks.

First of all, phone AI systems are based on enormous amounts of personal information — from location and biometrics (face, voice, fingerprints) to usage patterns of apps.
If such information is abused, leaked, or obtained illegally, businesses face heavy penalties under GDPR or CCPA, along with a bad reputation. Moreover, the more extensive the use of AI for real-time personalization, the higher the likelihood of exposure.
Security is also high on the list. Both on-device and cloud AI are susceptible to compromise through data tampering, adversarial input, or model inversion — attacks that try to extract or manipulate the internal data of the model.
Bias and transparency issues are no less important. AI models are trained from data that may have inherent biases, leading to unfair results in facial analysis, content recommendation, or hiring software.
Lastly, since many deep learning models are “black boxes,” it is often difficult to explain how decisions are made, which can cause problems with regulators and users.
And because laws typically lag behind technology, businesses that operate in extremely regulated industries are more likely to be fined, audited, and experience compliance matters if AI technologies are not managed responsibly.
Case Studies: AI in Leading Smartphones (2025 Edition)
Despite user concerns that remain a barrier to adoption, all smartphone market leaders are striving to integrate advanced AI features, whether on-device AI, cloud processing, or specialized hardware, such as neural processing units.
Apple
Apple is actively integrating AI into mobile devices through Apple Intelligence, which reinforces the iPhone with a smarter AI agent, writing tools, privacy-focused features, live translation, image playground, writing tools, and mail/message summary.
The company is also collaborating with OpenAI to integrate ChatGPT into its Apple Intelligence suite.
Major Apple AI-powered features include:
- Face ID: Deep learning for facial recognition with anti-spoofing.
- Live Text/Object & OCR: Extracts text from images and videos in real time.
- Camera Enhancements: Smart HDR, Night Mode, and computational photography rely on neural networks for scene detection, depth mapping, and noise reduction.
- Predictive Typing: Models analyze typing patterns to suggest the next words and emojis.
Google continues to lead in AI inventions with its Tensor chipset and deep integration of AI across the Pixel ecosystem.

The major artificial intelligence functions cover:
- Magic Eraser & Photo Enhancements: Remove objects and adjust lighting using deep learning.
- Call Screening: On-device speech recognition filters spam, while cloud NLP interprets complex requests.
- Real-Time Translation: Partly on-device for speed, with cloud support for more languages.
- Adaptive Battery & Performance: AI predicts app use to manage resources and save battery.
Samsung
Samsung is positioning its Galaxy AI platform as a central element of its device strategy. As key AI features, Samsung offers audio eraser, writing assist, transcript assist, browsing assist, call assist, and drawing assist.
The system integrates:
- Live Translation & AR: Computer vision models for object recognition, text & voice translation, and AR overlays.
- Smart Crop & Camera AI: Scene detection and low-light enhancement powered by neural networks, as well as photo editing (deletion, movement, addition of objects).
- Adaptive Battery & Resource Management: Predictive models adjust CPU/GPU load and background apps.
- Health & Biometric Monitoring: AI analyzes sensor data for heart rate, sleep, and stress tracking.
Huawei, OnePlus, and Xiaomi
Huawei, OnePlus, and Xiaomi are also heavily investing in AI to improve performance, personalization, and imaging.
Huawei’s XMAGE system uses advanced neural networks for color tuning and object detection, while its Kirin NPUs process tasks like voice commands and scene recognition offline.
OnePlus integrates AI into the OxygenOS environment to enable smart notifications, adaptive performance tuning, and improved photo clarity.
Xiaomi continues to advance its HyperOS AI features, introducing AI portrait enhancements, context-aware assistants, and battery optimization driven by on-device machine learning.
Future Trends & Innovation
The future of AI in mobile technologies is closely tied to the rise of intelligent devices in general. Just like AI PCs powered by NPUs, smartphones are now equipped with their own on-device AI chips.

Apple, Samsung, and Xiaomi are adding these capabilities not only to premium models but also to mid-range phones, which makes AI features available to a much wider audience.
On-device AI also reduces the need for constant cloud access, making phones faster, more private, and more energy-efficient.
AI is also spreading beyond smartphones into connected devices such as wearables, earbuds, and smart glasses. In the extended reality (XR) space, AI now powers live translation, gesture recognition, and 3D mapping, creating more immersive and responsive experiences.
Why Choose SCAND for AI Development?
At SCAND, we combine over 25 years of software development experience with deep expertise in AI technologies to help businesses build next-generation mobile solutions.
Our team provides comprehensive AI consulting and develops intelligent, high-performance apps powered by ML, computer vision, natural language processing, and on-device AI.
We work with both proprietary and open-source AI frameworks, integrating tools like TensorFlow Lite, Core ML, and ONNX Runtime Mobile for efficient on-device inference.
For clients who require full data control, we implement local large language models (LLMs) such as LLaMA or Mistral, and use Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipelines to deliver more accurate, context-aware results.
SCAND’s approach covers the entire development lifecycle — from AI strategy and architecture design to machine learning development, model fine-tuning, testing, and deployment.
Whether it’s building privacy-focused AI features, integrating edge computing, or optimizing model performance, we guarantee the best possible output.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What does AI do in smartphones?
AI in smartphones helps devices understand, learn, and adapt to user behavior. It powers camera optimization, voice assistants, predictive text, and app suggestions. By processing data through on-device AI chips, phones can deliver smarter and more energy-efficient performance.
What is an NPU and why is it important?
An NPU, or Neural Processing Unit, is a dedicated chip designed specifically for running AI and ML tasks. Unlike traditional CPUs or GPUs, NPUs process data in parallel, which speeds up AI operations such as photo processing or facial recognition.
How is Edge AI different from cloud AI?
Edge AI processes data directly on the smartphone rather than sending it to remote servers. Cloud AI, on the other hand, is better suited for large-scale data analysis or tasks that require more computing power.
How does AI improve mobile marketing and business applications?
AI allows businesses to analyze user data, predict behavior, and suggest highly personalized ads. It also enables smarter app design, real-time analytics, and adaptive interfaces. Marketers use AI for automated campaigns, voice search optimization, and conversational engagement to boost customer interaction.
Are there privacy risks with AI in phones?
Unfortunately, yes. Privacy still remains a problem. AI applications rely on user data for learning, which raises risks of misuse or unauthorized access.
What does the future hold for AI in smartphones?
Future smartphones will use more powerful AI chips and integrate generative AI to provide proactive assistance, such as predicting user needs, automating tasks, and enabling real-time creativity.